Understanding Blockchain Bridges: Complete Guide 2026
Learn how crypto bridges work, types of bridges, security considerations, and how to safely bridge tokens across different blockchains.
What Are Blockchain Bridges?
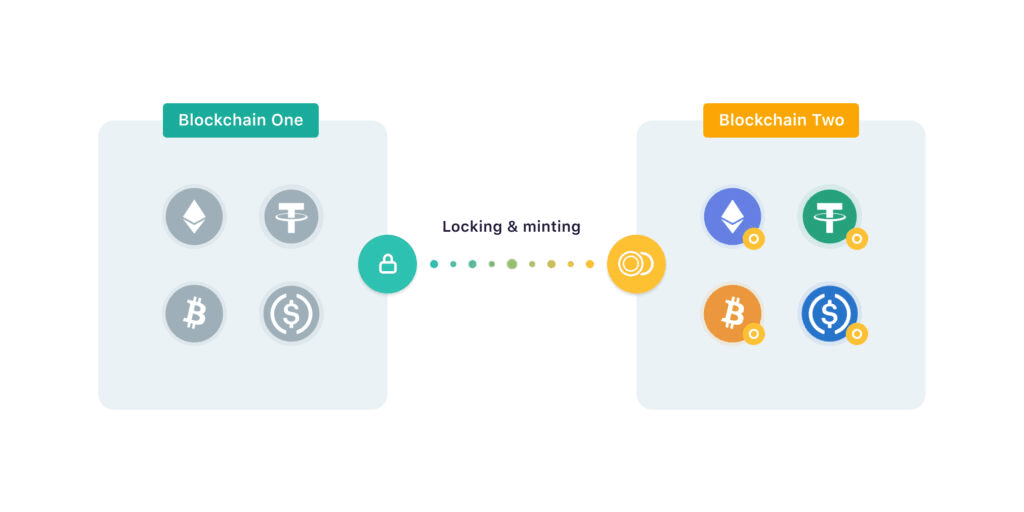
Blockchain bridges are protocols that enable the transfer of tokens, data, and smart contract instructions between different blockchain networks. They solve one of crypto's biggest challenges: blockchain interoperability.
Think of bridges as connectors between isolated islands (blockchains), allowing assets and information to flow freely between them.
Why Do We Need Bridges?
The Blockchain Isolation Problem
Each blockchain network operates independently with its own:
- Native tokens
- Transaction rules
- Smart contract capabilities
- Security mechanisms
- Consensus protocols
Without bridges, Bitcoin exists only on Bitcoin's network, Ethereum tokens stay on Ethereum, and Solana assets remain on Solana. This creates siloed ecosystems that can't communicate or share value.
Bridge Benefits
For Users:
- Access DeFi opportunities across multiple chains
- Avoid high gas fees by moving to cheaper networks
- Participate in ecosystems without selling existing holdings
- Diversify holdings across multiple chains
For the Ecosystem:
- Increased liquidity across all chains
- Broader adoption of emerging networks
- More competitive fee markets
- Enhanced innovation and composability
How Do Bridges Work?
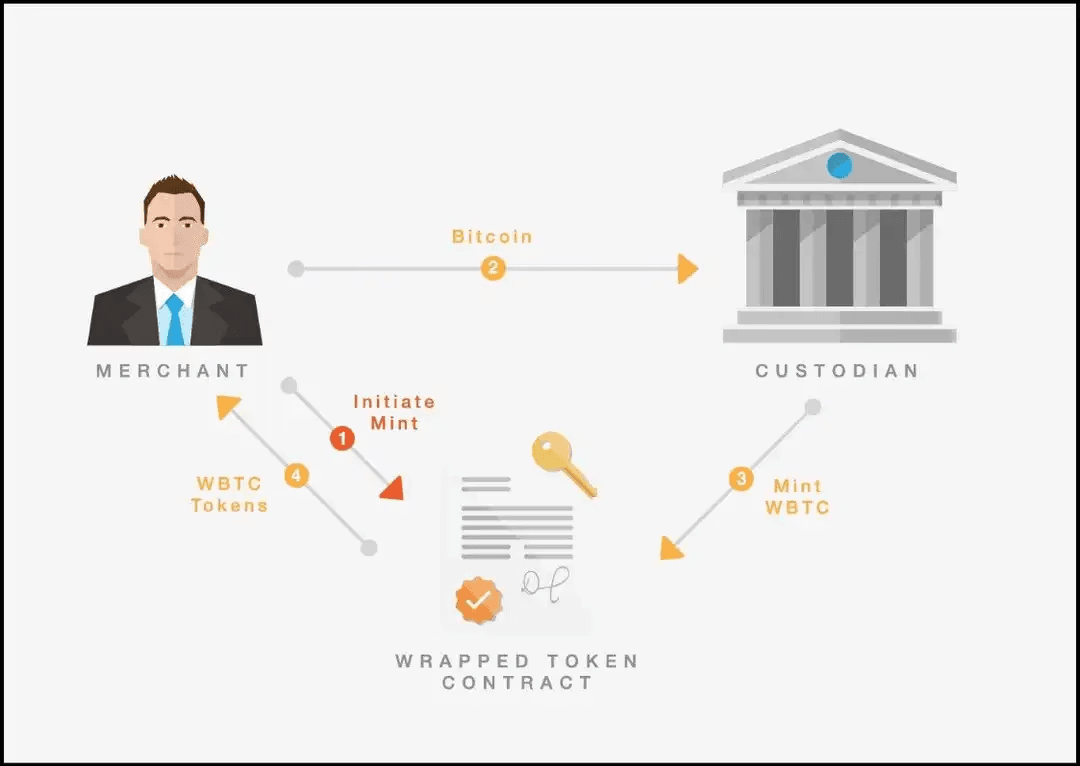
The Lock-and-Mint Model
This is the most common bridging mechanism:
- Lock: You deposit tokens on the source chain into a smart contract
- Verify: The bridge verifies your deposit
- Mint: Equivalent tokens are minted on the destination chain
- Receive: You receive the bridged tokens in your wallet
When bridging back, the process reverses:
- Burn wrapped tokens on the destination chain
- Unlock original tokens on the source chain
The Liquidity Pool Model
Some bridges use liquidity pools on both chains:
- You deposit tokens into a pool on the source chain
- Equivalent tokens are released from a pool on the destination chain
- No minting/burning required
- Faster but requires sufficient liquidity
Types of Blockchain Bridges
1. Custodial vs. Non-Custodial
Custodial Bridges:
- Third party controls your funds during bridging
- Faster execution
- Single point of failure
- Examples: Centralized exchange bridges
Non-Custodial Bridges:
- You maintain control via smart contracts
- More decentralized
- Trustless operation
- Examples: Most DeFi bridges
2. Unidirectional vs. Bidirectional
Unidirectional:
- One-way transfers only
- Simpler design
- Lower risk
Bidirectional:
- Transfer assets in both directions
- More flexible
- More complex
3. Single-Chain vs. Multi-Chain
Single-Chain Bridges:
- Connect two specific blockchains
- Optimized for that pair
- Example: Polygon Bridge (Ethereum ↔ Polygon)
Multi-Chain Bridges:
- Support multiple blockchain networks
- More versatile
- Example: Pouch Swap (45+ networks)
Popular Bridge Examples
Ethereum-Centric Bridges
Polygon Bridge
- Connects Ethereum and Polygon
- Official bridge for MATIC network
- High security, moderate speed
Arbitrum Bridge
- Ethereum to Arbitrum L2
- Built for scaling
- Inherited Ethereum security
Cross-Ecosystem Bridges
Wormhole
- Connects Ethereum, Solana, BSC, and more
- Focus on speed
- Large TVL (Total Value Locked)
Rainbow Bridge
- Ethereum to NEAR Protocol
- Trustless design
- Community-built
Security Considerations
Bridge Risks
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities:
- Bugs in bridge code can be exploited
- Always check audit reports
- Use bridges with proven track records
Validator/Oracle Risks:
- Compromised validators can approve fraudulent transfers
- Decentralized validator sets are safer
Liquidity Risks:
- Insufficient liquidity can delay bridging
- Large transfers may experience slippage
Wrapped Token Risks:
- Wrapped tokens are IOUs, not native assets
- Depends on bridge's solvency and security
Historic Bridge Hacks
Learning from past incidents:
Ronin Bridge (2022): $600M+ stolen
- Lesson: Validator security is critical
Wormhole (2022): $320M exploit
- Lesson: Code audits must be thorough
Nomad Bridge (2022): $200M drained
- Lesson: Smart contract testing is essential
How to Use Bridges Safely
Before Bridging
✅ Research the Bridge
- Check security audits
- Review TVL and bridge age
- Read user reviews
✅ Understand the Tokens
- Know what you're receiving (wrapped vs. native)
- Verify token contract addresses
- Check liquidity on destination chain
✅ Calculate Total Costs
- Source chain gas fees
- Bridge fees
- Destination chain gas fees
- Price impact/slippage
During Bridging
✅ Start Small
- Test with minimal amounts first
- Verify receipt before large transfers
✅ Double-Check Addresses
- Ensure destination address is correct
- Confirm network selection
- Never bridge to exchange deposit addresses
✅ Be Patient
- Bridges can take 10-60 minutes
- Don't panic if confirmation is delayed
- Save transaction hashes
After Bridging
✅ Verify Receipt
- Check destination wallet
- Confirm correct token amount
- Verify token contract
✅ Keep Records
- Save transaction IDs
- Note timestamps
- Document any issues
Bridging on Pouch Swap
Pouch Swap simplifies bridging with:
Multi-Chain Support
45+ blockchain networks including:
- Ethereum, BSC, Polygon
- Arbitrum, Optimism, Base
- Solana, Avalanche, Fantom
- And many more
No Account Required
- No KYC/registration
- Start bridging immediately
- Complete privacy
Best Rates
- Aggregates multiple bridge sources
- Automatic route optimization
- Transparent fee structure
Simple Process
- Select source and destination chains
- Enter amount and wallet address
- Confirm details
- Send tokens
- Receive bridged assets (5-30 minutes)
Future of Blockchain Bridges
Emerging Trends
Layer Zero Protocol:
- Omnichain interoperability
- Message passing between chains
- Next-gen bridge technology
Chain Abstraction:
- Users don't need to know which chain they're on
- Seamless multi-chain experience
- Background bridging
Improved Security:
- Formal verification of bridge code
- Decentralized validator networks
- Insurance protocols for bridge risk
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between bridging and swapping?
Bridging transfers the same token between chains (e.g., USDT from Ethereum to Polygon). Swapping exchanges one token for another (e.g., BTC to ETH).
Are bridged tokens the same as native tokens?
Bridged tokens are usually "wrapped" versions (wBTC, WETH, etc.) that represent native tokens. They function the same but are technically different contracts.
How long does bridging take?
Typically 5-30 minutes, though it can take longer during high network congestion or for certain chain combinations.
Can bridged tokens be bridged back?
Yes, most bridges support bidirectional transfers. You can bridge back to the original chain at any time.
Conclusion
Blockchain bridges are essential infrastructure for the multi-chain future of crypto. While they introduce new risks, understanding how they work and following best practices allows you to safely access opportunities across all blockchain ecosystems.
As bridge technology improves, expect faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-chain transfers - eventually making chain selection as seamless as choosing between apps.
Want to bridge tokens safely? Try Pouch Swap's multi-chain bridge supporting 45+ networks with no account required.
Join our Telegram community to discuss bridges and get help.
Share this article: