Bridges vs Swaps in 2026: Complete Guide to Cross-Chain Crypto Transfers
Comprehensive 2026 guide comparing crypto bridges vs swaps. Learn when to use each method, security risks, costs, and best practices for cross-chain transfers.
The Multi-Chain Reality of 2026
Welcome to the new normal: blockchain ecosystems are no longer isolated islands. In 2026, sophisticated crypto users navigate seamlessly between Ethereum, Solana, BSC, Avalanche, and dozens of other networks daily.
The multi-chain era is here to stay, and with it comes a fundamental question that every crypto user must answer:
How do I move assets between different blockchain networks efficiently and safely?
The answer isn't simple. You have two primary options: crypto bridges and crypto swaps. Each serves different purposes, offers unique advantages, and carries specific risks.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand when to use each method, how they work, and which is right for your specific needs.
Quick Answer: When to Use Each
Use Crypto Bridges When:
- Same token, different chain (e.g., USDT Ethereum → USDT Polygon)
- Accessing specific DeFi protocols on other chains
- Moving large amounts where liquidity matters
- Need wrapped tokens for ecosystem participation
- Timing isn't critical (10-60 minutes acceptable)
Use Crypto Swaps When:
- Different tokens, possibly different chains (e.g., BTC → ETH)
- Speed is essential (need completion in minutes)
- Privacy is priority (no KYC, no account)
- Simplicity matters (one-step process)
- Small to medium amounts (under $100,000)
Pouch Swap combines both - you can swap across chains in a single transaction.
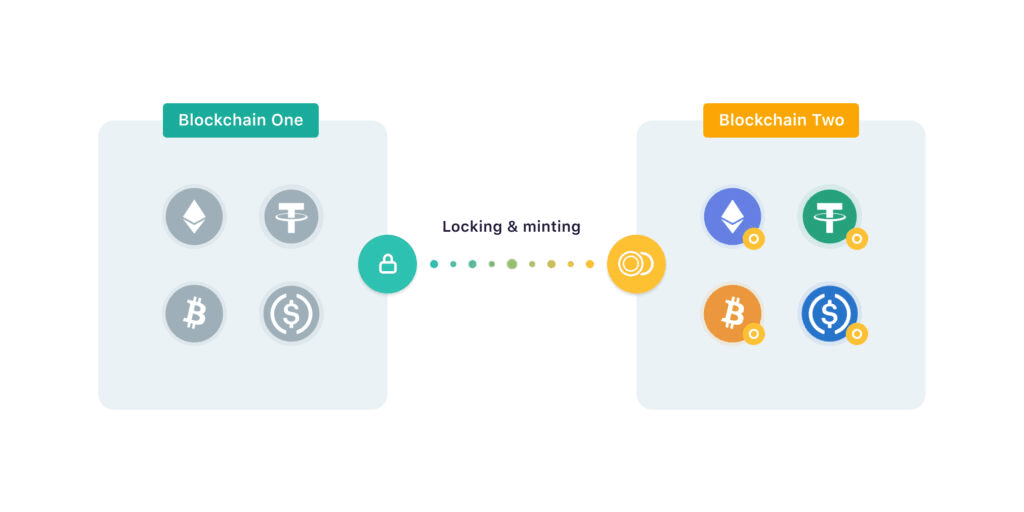
Understanding Crypto Bridges
What Are Crypto Bridges?
Crypto bridges are protocols that connect two or more blockchain networks, enabling the transfer of assets and data between them. Think of them as digital highways linking separate crypto cities.
Core Function:
- Transfer the same token between different blockchains
- Usually create "wrapped" versions of tokens
- Maintain 1:1 backing (ideally)
- Enable cross-chain DeFi operations
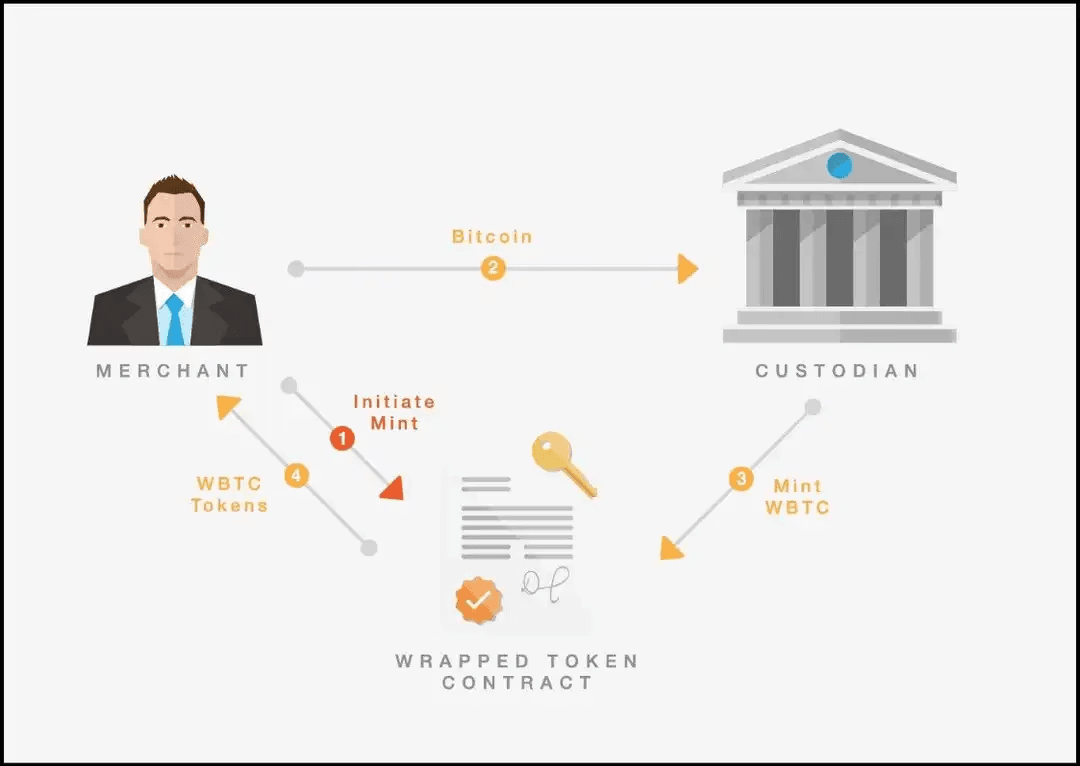
How Bridges Work: The Technical Side
Lock-and-Mint Mechanism
This is the most common bridging method:
- Lock: You deposit tokens into a smart contract on Chain A
- Verify: Bridge validators confirm the lock transaction
- Mint: Equivalent tokens are created (minted) on Chain B
- Release: You receive minted tokens in your destination wallet
Example: Bridging USDT from Ethereum to Polygon
- USDT locked in Ethereum smart contract
- Polygon validators confirm Ethereum transaction
- USDT minted on Polygon network
- You receive Polygon USDT in your wallet
Burn-and-Unlock (Return Journey)
When bridging back:
- Burn: Wrapped tokens are destroyed on Chain B
- Verify: Bridge confirms burn transaction
- Unlock: Original tokens released from Chain A contract
- Receive: Original tokens arrive in source wallet
Types of Crypto Bridges
By Trust Model
Custodial Bridges:
- Centralized entity controls tokens during transfer
- Examples: Exchange bridges (Binance Bridge, Coinbase Bridge)
- Pros: Fast, user-friendly
- Cons: Trust required, single point of failure
Non-Custodial Bridges:
- Smart contracts control the entire process
- Examples: Wormhole, Multichain, Stargate
- Pros: Trustless, decentralized
- Cons: More complex, potential smart contract risks
By Directionality
Unidirectional Bridges:
- Assets flow one way only (A → B)
- Simpler architecture, lower risk
- Example: Some early Bitcoin-to-Ethereum bridges
Bidirectional Bridges:
- Two-way transfers supported (A ↔ B)
- More complex but versatile
- Example: Most modern bridges
By Scope
Single-Chain Bridges:
- Connect two specific networks
- Optimized for that pair
- Example: Polygon POS Bridge (Ethereum ↔ Polygon)
Multi-Chain Bridges:
- Support multiple blockchain networks
- More flexible routing
- Example: Pouch Swap (45+ networks), LayerZero
Understanding Crypto Swaps
What Are Crypto Swaps?
Crypto swaps are instant exchanges of one cryptocurrency for another, typically without requiring user registration or custodial accounts. They focus on changing assets, not moving them between chains.
Core Function:
- Exchange different tokens
- Often across different blockchain networks
- Instant rate discovery
- Non-custodial execution
How Swaps Work: The Mechanics
Direct Swap Method
- User Selection: Choose token pair (e.g., BTC → ETH)
- Rate Discovery: Platform finds best exchange rate
- Address Generation: Platform provides destination addresses
- User Deposit: User sends source token to provided address
- Exchange Execution: Platform exchanges tokens
- Destination Transfer: Target tokens sent to user's wallet
Cross-Chain Swap Method
When tokens are on different chains:
- Rate Lock: Exchange rate is fixed temporarily
- Source Transfer: User sends tokens (Chain A)
- Bridge Execution: Platform automatically bridges to Chain B
- Swap Execution: Exchange completed on Chain B
- Delivery: Target tokens sent to user's wallet (Chain B)
Key Innovation: Modern platforms like Pouch Swap combine bridging and swapping in a single transaction.
Types of Crypto Swaps
By Execution Model
Atomic Swaps:
- Exchange happens atomically or not at all
- Either both transfers complete or neither does
- Highest security but limited token support
DEX Aggregator Swaps:
- Multiple DEXes searched for best rates
- Split trades across platforms for optimal pricing
- Most common in 2026
By Custody
Custodial Swaps:
- Platform temporarily controls funds
- Examples: Changelly, ShapeShift (historically)
- Pros: More token pairs, competitive rates
- Cons: Trust required
Non-Custodial Swaps:
- Smart contracts handle the exchange
- User maintains control throughout
- Examples: Pouch Swap, 1inch
- Pros: Trustless, secure
- Cons: Limited to certain token pairs
Head-to-Head Comparison
Speed Comparison
| Method | Typical Time | Best Case | Worst Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge | 10-30 minutes | 2-5 minutes | 2+ hours |
| Swap | 5-15 minutes | 1-3 minutes | 30+ minutes |
| Pouch Swap | 5-10 minutes | 2-5 minutes | 15-20 minutes |
Cost Comparison
| Method | Typical Cost Range | Cost Components |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge | 0.1% - 1.0% | Bridge fee + destination gas |
| Swap | 0.2% - 0.8% | Exchange spread + network fees |
| Pouch Swap | 0.3% - 0.6% | Aggregated rate + optimized routing |
Security Comparison
| Factor | Bridges | Swaps | Pouch Swap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Contract Risk | Medium | Low | Low |
| Custodial Risk | Varies | Varies | None |
| Historic Exploits | $2B+ lost | $200M+ lost | None |
| Auditing | Inconsistent | Good | Comprehensive |
Security Considerations
Bridge Security Risks
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
- Code bugs can lead to complete loss
- Upgrade risks when contracts are modified
- Oracle manipulation affecting price feeds
Validator/Oracle Issues
- Centralized validators can collude
- Price oracle failures causing incorrect conversions
- Network congestion leading to failed transactions
Liquidity Risks
- Insufficient liquidity causing failed bridges
- Large slippage on big transactions
- Imbalanced pools affecting rates
Historic Bridge Hacks:
- Wormhole (2022): $320M stolen
- Ronin Bridge (2022): $600M+ exploit
- Nomad Bridge (2022): $200M drained
- Multichain (2023): $125M suspicious activity
Swap Security Risks
Front-Running Attacks
- MEV bots exploiting swap transactions
- Sandwich attacks increasing costs
- Slippage manipulation in mempool
Rate Manipulation
- False price feeds showing bad rates
- Hidden fees not clearly displayed
- Exchange rate spreads wider than shown
Smart Contract Risks
- Unauthorized token approvals
- Reentrancy attacks on swap contracts
- Flash loan exploits
Use Case Deep Dive
When Bridges Are Better
DeFi Protocol Access
Scenario: You want to use Aave lending on Polygon, but your USDC is on Ethereum.
Solution: Bridge USDC from Ethereum to Polygon
- Cost: ~0.1% bridge fee + gas
- Time: 10-20 minutes
- Result: Native Polygon USDC for Aave
Large Amount Transfers
Scenario: Moving $500,000 from Ethereum to BSC for better yield.
Solution: Bridge directly rather than swapping
- Cost: 0.3% bridge fee ($1,500)
- Better than: Swap fees + gas on both chains
- Liquidity guaranteed for large amounts
Ecosystem Participation
Scenario: Participating in Solana NFT mint, but funds are on Ethereum.
Solution: Bridge ETH to Solana via wrapped ETH (wETH)
- Access Solana-specific opportunities
- Maintain Ethereum asset exposure
- Lower fees on Solana network
When Swaps Are Better
Market Volatility Response
Scenario: Bitcoin crashing 15% in 2 hours, need stablecoin exposure fast.
Solution: Swap BTC → USDT on Pouch Swap
- Time: 5-10 minutes
- No KYC delays
- Immediate rate lock
- Non-custodial throughout
Privacy Requirements
Scenario: Need to exchange crypto without revealing identity.
Solution: Use non-custodial swap platform
- No registration required
- No personal data collection
- Transaction appears as normal crypto transfer
Cross-Chain Token Exchange
Scenario: Have BTC on Bitcoin network, want ETH on Ethereum.
Solution: Direct cross-chain swap
- BTC (Bitcoin) → ETH (Ethereum)
- Single transaction handles bridge + swap
- Simplified process vs. separate operations
Advanced Strategies
Multi-Chain Yield Farming
Strategy: Use bridges for access, swaps for optimization
-
Initial Setup
- Bridge stablecoins to 3-4 different chains
- Maintain liquidity across ecosystems
- Ready to capitalize on opportunities
-
Opportunity Capture
- Find high-yield opportunity on new chain
- Bridge initial capital quickly
- Use swaps for token adjustments
- Maximize returns across chains
-
Risk Management
- Diversify across multiple bridges
- Use time-locked strategies
- Monitor gas costs vs. yields
Arbitrage Opportunities
Cross-Chain Arbitrage:
- Identify Price Difference: Same token priced differently across chains
- Calculate Net Profit: Bridge fees + swap fees + gas = total cost
- Execute Strategy: Bridge to cheaper chain, swap, bridge back
- Timing Critical: Price differences often resolve quickly
Pouch Swap Advantage:
- Real-time rate comparison across chains
- Optimal routing automatically calculated
- Single interface for complex arbitrage
- Reduced execution time increases success rate
Portfolio Rebalancing
Traditional Method:
- Bridge to centralized exchange
- Execute trades on exchange
- Bridge results back to desired chains
- Time: 2-3 hours, multiple custodians
Modern Method:
- Use Pouch Swap for cross-chain rebalancing
- Direct target-to-target exchanges
- Non-custodial throughout
- Time: 15-30 minutes total
The Pouch Swap Hybrid Approach
Combining Best of Both Worlds
Pouch Swap represents the evolution of both technologies:
Bridge Capabilities:
- 45+ blockchain networks supported
- Wrapped token creation when needed
- Cross-chain liquidity pools
- Automatic route optimization
Swap Advantages:
- Instant exchange rates from multiple sources
- Non-custodial execution
- No registration or KYC required
- Competitive fee structures
Technical Innovation:
- Unified Interface: One platform handles both needs
- Smart Routing: AI selects optimal bridge+swap combination
- Risk Minimization: Audited smart contracts + multiple liquidity sources
- Speed Optimization: Parallel processing reduces total time
Example: Complex Cross-Chain Swap
User Goal: Convert BTC on Bitcoin network to USDC on Arbitrum
Traditional Method:
- Bridge BTC to Ethereum (30 minutes)
- Swap BTC for ETH on DEX (15 minutes)
- Bridge ETH to Arbitrum (20 minutes)
- Swap ETH for USDC on Arbitrum DEX (10 minutes) Total Time: ~75 minutes, 4 platforms, 3 custody transfers
Pouch Swap Method:
- Select BTC → USDC (Arbitrum)
- Platform finds optimal route: BTC → ETH → Arbitrum → USDC
- Single transaction executes entire path Total Time: 10-15 minutes, 1 platform, 0 custody
Future Trends: 2026 and Beyond
Interoperability Evolution
Current State (2026):
- Multiple successful bridges and swaps
- Growing standardization
- Improved security practices
- Better user experience
Near Future (2027-2028):
- Chain abstraction: Users don't need to know which chain they're using
- Universal bridges: One protocol to connect all chains
- Zero-knowledge transfers: Enhanced privacy for all cross-chain transactions
- AI-optimized routing: Real-time optimal path discovery
Long-term Vision (2029+):
- Seamless multi-chain experience: Chains invisible to end users
- Instant finality: Cross-chain transactions completing in seconds
- Quantum-resistant security: Protecting long-term cross-chain value
- DeFi composability: Any protocol can use any asset from any chain
Regulatory Considerations
Increasing Scrutiny:
- Bridge regulations developing globally
- Swap platform licensing requirements emerging
- Privacy vs. KYC balance being debated
- Cross-border transaction monitoring expanding
Compliance Strategies:
- Decentralized governance for decision making
- Geographic restrictions implemented responsibly
- Privacy options maintained where legal
- Audit transparency for regulatory compliance
Best Practices for 2026
Security Checklist
Before Any Bridge/Swap:
- ✅ Verify platform reputation and track record
- ✅ Check smart contract audits and security reviews
- ✅ Understand token differences (wrapped vs. native)
- ✅ Calculate total costs including all fees
- ✅ Test with small amounts first
- ✅ Verify all addresses before confirming
During Execution:
- ✅ Double-check network selection
- ✅ Monitor gas fees and adjust timing if needed
- ✅ Save transaction hashes for tracking
- ✅ Be patient with confirmation times
After Completion:
- ✅ Verify receipt in destination wallet
- ✅ Confirm token amounts and contracts
- ✅ Update portfolio records
- ✅ Security sweep of used wallets if necessary
Cost Optimization Strategies
Minimize Fees:
- Bridge to Layer 2s for lower gas costs
- Use native tokens when possible (avoid wrapped versions)
- Batch transactions when making multiple transfers
- Monitor gas price trackers for optimal timing
Maximize Value:
- Compare rates across multiple platforms
- Consider total costs not just exchange rates
- Factor in time costs for time-sensitive transfers
- Use loyalty programs when available
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is safer: bridges or swaps?
Bridges have historically seen larger exploits ($2B+ vs $200M+), but swaps expose you to different risks like front-running and MEV attacks. Both require careful platform selection and security practices.
Can I get stuck during a bridge or swap?
Yes, but rarely on reputable platforms. Bridges can get stuck if there's insufficient liquidity or network congestion. Swaps can fail if rates change dramatically during execution. Always test with small amounts first.
Do I pay taxes on cross-chain transfers?
Tax treatment varies by jurisdiction, but most countries treat:
- Bridges: Like transfers between your own accounts (non-taxable event)
- Swaps: Like trades (potentially taxable event)
- Consult tax professionals for your specific situation
What happens if a bridge gets hacked?
If you have funds on a bridge when it gets hacked:
- Custodial bridges: May have insurance or partial recovery
- Non-custodial bridges: Typically total loss unless you withdrew before exploit
- Importance: Use bridges with strong security and insurance
Why are swap rates sometimes different from exchange rates?
Swap rates include:
- Exchange spread between bid/ask prices
- Liquidity costs for providing instant execution
- Network fees for blockchain transactions
- Platform fees for the service
Making Your Choice
Decision Framework
Choose Bridges If:
- Same token, different chain
- Large amounts (>$50,000)
- Accessing specific DeFi protocols
- Time not critical (15+ minutes acceptable)
Choose Swaps If:
- Different tokens (possibly same chain)
- Speed essential (under 10 minutes)
- Privacy required (no KYC)
- Simplicity valued
Choose Pouch Swap If:
- Complex cross-chain needs
- Best rates across all options
- Single platform preference
- Maximum security and privacy
Getting Started
For Beginners:
- Start with swaps for simple token exchanges
- Learn bridge basics with small amounts
- Use reputable platforms with good reviews
- Gradually expand to more complex operations
For Advanced Users:
- Diversify across platforms
- Optimize for cost and speed
- Utilize advanced strategies like arbitrage
- Stay updated on new protocols and security practices
Conclusion
The multi-chain future is here, and understanding both bridges and swaps is essential for every crypto user in 2026.
Bridges excel at moving the same token between networks, enabling ecosystem participation and large transfers efficiently.
Swaps dominate when you need to exchange different tokens quickly, privately, and simply.
Pouch Swap represents the convergence of both technologies, offering intelligent routing that automatically selects the optimal combination of bridging and swapping for your specific needs.
The key is understanding your specific requirements - speed, cost, privacy, or simplicity - and choosing the method that best serves those needs.
As crypto continues evolving toward seamless interoperability, platforms that combine both bridges and swaps will become the standard. Pouch Swap is leading this evolution today.
Ready to experience the future of cross-chain crypto transfers?
Try Pouch Swap's Unified Bridge & Swap Platform
Master cross-chain crypto transfers with confidence. Join our Telegram community for expert tips and real-time support.
Share this article: